Warning: Cannot modify header information - headers already sent in /home/u278635817/domains/myhousegarden.com/public_html/wp-content/plugins/artigosgpt/artigosgpt.php on line 28454
Imagine transforming your outdoor space into a vibrant, sustainable sanctuary that not only beautifies your home but also nurtures the planet. Eco landscaping is more than just a gardening trend—it’s a commitment to creating environments that harmonize with nature while enhancing your everyday living.
In today’s world, where environmental concerns are paramount, eco landscaping has emerged as a crucial approach to reduce water waste, minimize chemical use, and support local ecosystems. This method merges aesthetics with sustainability, offering a garden that thrives responsibly.
In this article, you will discover innovative eco-friendly garden designs that inspire and empower you to cultivate your own sustainable paradise. From design principles to practical steps, let’s explore how eco landscaping can transform your home and the environment.
Understanding the Core Principles of Eco Landscaping
What Defines Eco Landscaping?
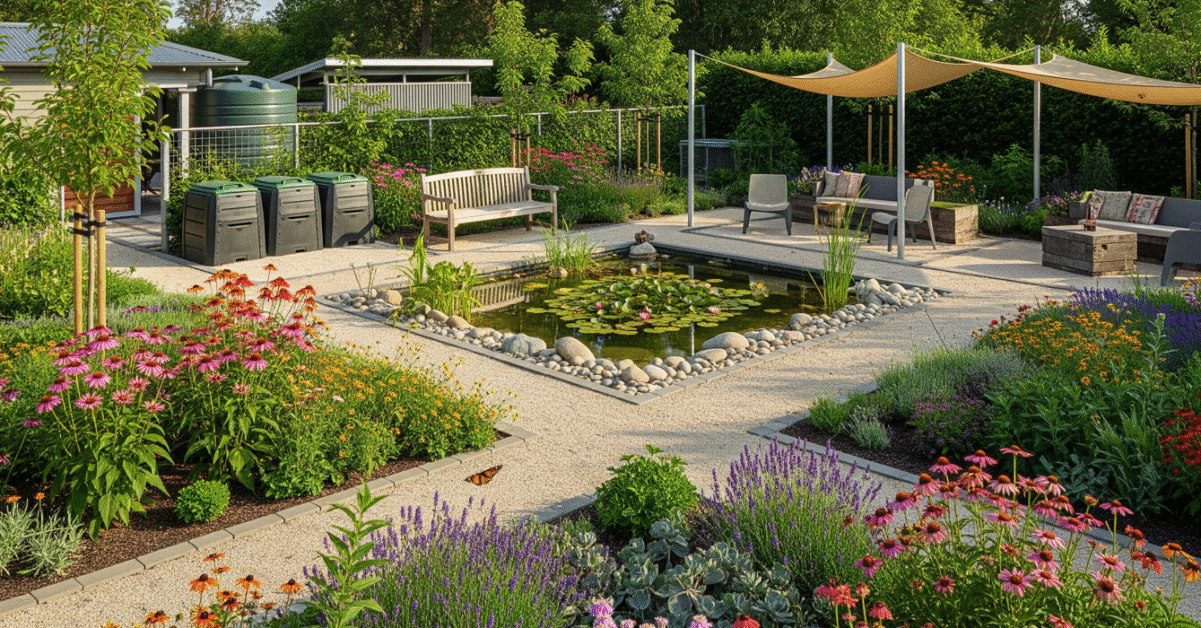
Eco landscaping focuses on sustainable garden practices that protect natural resources. It emphasizes native plants, water conservation, and soil health to foster a balanced ecosystem around your home.
This approach reduces environmental impact while creating beautiful, functional outdoor spaces that require fewer resources and less maintenance.
Key Benefits of Eco-Friendly Gardens
Beyond beauty, eco landscaping conserves water, supports pollinators, and improves air quality. It also lowers energy costs by providing shade and reducing heat absorption.
These benefits contribute to a healthier environment and enhance the quality of life for homeowners and wildlife alike.
Integrating Sustainability and Aesthetics
Successful eco landscaping blends visual appeal with ecological responsibility. Using diverse plant species and natural materials creates inviting spaces that thrive with minimal intervention.
The balance between design and nature promotes resilience and long-term sustainability in your garden.
Choosing Native and Drought-Tolerant Plants
Why Native Plants Matter
Native plants are adapted to local climates and soils, requiring less water and fewer chemicals. They provide essential habitat for local wildlife and support biodiversity.
Incorporating native species helps your garden flourish naturally and reduces maintenance efforts.
Benefits of Drought-Tolerant Species
Drought-tolerant plants conserve water by thriving in dry conditions. They reduce irrigation needs, saving resources and lowering your water bills.
These resilient plants keep your garden vibrant even during dry spells or water restrictions.
Mixing Varieties for Year-Round Interest
Combine native and drought-tolerant plants with evergreens, perennials, and ground covers. This diversity ensures visual appeal and ecological balance throughout the seasons.
A layered planting scheme creates texture, color, and habitat diversity in your eco-friendly garden.
Efficient Water Management Techniques
Rainwater Harvesting Systems
Collecting rainwater reduces dependence on municipal supplies. Rain barrels and cisterns provide an eco-friendly irrigation source for your landscape.
This practice conserves water and helps manage runoff, preventing erosion and pollution.
Drip Irrigation and Smart Controllers
Drip irrigation delivers water directly to plant roots, minimizing waste. Smart controllers adjust watering based on weather and soil conditions.
These technologies optimize water use, ensuring plants receive just the right amount for healthy growth.
Creating Natural Water Features
Ponds, swales, and rain gardens capture and filter water naturally, supporting wildlife and improving soil moisture.
These features enhance garden aesthetics while promoting sustainable water cycles within your property.
Soil Health and Organic Practices
Building Fertile Soil Naturally
Healthy soil is the foundation of eco landscaping. Adding organic matter like compost improves nutrient content and water retention.
This supports robust plant growth and enhances resilience against pests and diseases.
Reducing Chemical Inputs
Minimizing synthetic fertilizers and pesticides protects soil microbes and local water sources. Organic alternatives nourish plants without harmful side effects.
This approach fosters a balanced ecosystem where beneficial insects and earthworms thrive.
Mulching for Moisture and Weed Control
Mulch conserves moisture, regulates soil temperature, and suppresses weeds naturally. Organic mulches break down over time, enriching the soil.
Using mulch reduces labor and water needs, making garden care more sustainable.
Designing for Wildlife and Pollinators
Creating Habitats with Native Plants
Native flowers, shrubs, and trees provide food and shelter for birds, bees, and butterflies. A diverse planting plan supports a healthy local ecosystem.
Encouraging wildlife increases pollination and pest control, benefiting your entire landscape.
Installing Birdhouses and Insect Hotels
Structures like birdhouses and insect hotels offer safe nesting sites, boosting beneficial species populations.
These additions add charm and functionality, connecting you closer to nature.
Water Sources for Wildlife
Shallow birdbaths and small ponds supply water to pollinators and birds. Clean, accessible water supports their survival during dry periods.
Incorporating these features enhances biodiversity and garden vitality.
Incorporating Sustainable Hardscaping Materials
Natural Stone and Reclaimed Wood
Using natural or recycled materials reduces environmental impact. Stone and reclaimed wood create durable, eco-conscious paths and seating areas.
These elements blend seamlessly with the garden, adding character and sustainability.
Permeable Paving Solutions
Permeable surfaces allow water to seep through, reducing runoff and replenishing groundwater.
Materials like gravel, porous concrete, or permeable pavers support eco-friendly drainage systems.
Solar Lighting and Energy Efficiency
Solar-powered garden lights cut electricity use while enhancing nighttime ambiance. Energy-efficient features complement your eco landscaping goals.
This lighting integrates sustainability without sacrificing style or safety.
Step-by-Step Guide to Starting Your Eco Landscaping Project
- Assess your site’s soil, sun exposure, and existing vegetation.
- Plan your garden layout focusing on native and drought-tolerant plants.
- Install water-efficient irrigation like drip systems or rainwater harvesting.
- Amend soil with organic compost and apply mulch to conserve moisture.
- Add wildlife-friendly features such as birdhouses and pollinator plants.
- Choose sustainable hardscaping materials and install permeable pathways.
Measuring Success and Maintaining Your Eco Landscape
Tracking Water and Resource Savings
Monitor your garden’s water usage before and after implementation. Notice reductions in irrigation needs and fertilizer use.
These metrics indicate your eco landscaping’s environmental and financial benefits.
Seasonal Maintenance Tips
Prune native plants appropriately and refresh mulch annually. Adjust irrigation schedules to seasonal changes for optimal health.
Regular care ensures your garden remains sustainable and visually appealing year-round.
Adapting and Expanding Your Eco-Friendly Garden
Observe your garden’s evolving ecosystem and introduce new native species or features. Continuously improve your landscape’s sustainability.
This adaptive approach strengthens resilience and fosters long-term ecological harmony.
| Eco Landscaping Element | Benefit | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Native Plants | Supports biodiversity and reduces water use | Milkweed, Coneflower, Blueberry Bush |
| Rainwater Harvesting | Conserves water and reduces runoff | Rain barrels, cisterns |
| Permeable Paving | Improves drainage and prevents erosion | Gravel paths, porous concrete |
| Organic Mulch | Improves soil health and moisture retention | Wood chips, leaf litter |
| Solar Lighting | Reduces energy consumption | Solar garden lamps |
Conclusion: Embrace the Beauty and Responsibility of Eco Landscaping
Eco landscaping invites you to reconnect with nature by crafting a garden that nurtures both your home and the environment. By integrating sustainable practices, native plants, and thoughtful design, you create a living space full of beauty, life, and purpose.
As you embark on this journey, remember that every step towards eco-friendly gardening is a step towards a healthier planet. Let your landscape be a testament to the harmony between human creativity and ecological stewardship.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main difference between eco landscaping and traditional landscaping?
Eco landscaping prioritizes sustainability by using native plants, conserving water, and reducing chemical inputs, while traditional landscaping often focuses on aesthetics without necessarily considering environmental impact. Eco landscaping aims to create balanced ecosystems that support local wildlife and reduce resource consumption.
How can I start an eco-friendly garden if I have limited space?
Even small spaces can benefit from eco landscaping by choosing container-friendly native plants, implementing vertical gardening, and using water-efficient irrigation. Focus on quality over quantity by selecting species that support pollinators and require minimal maintenance.
Are native plants more expensive or harder to maintain?
Native plants are generally cost-effective and low-maintenance because they are adapted to local conditions. They need less water, fertilizer, and pesticides compared to non-native species, which often require more resources to thrive.
Can eco landscaping help reduce my home’s energy bills?
Yes. Strategic placement of trees and shrubs provides natural shade and wind protection, reducing cooling and heating costs. Additionally, using native plants reduces water and maintenance expenses, contributing to overall savings.
What are some common mistakes to avoid in eco landscaping?
Avoid choosing invasive or non-native plants, overwatering, and relying heavily on chemical fertilizers or pesticides. Planning without considering local climate and soil conditions can also reduce success. Proper research and design tailored to your environment are essential.
For further inspiration and detailed guides, visit EPA Green Infrastructure and Audubon Native Plants Database.